Electronic devices manufactured today tend to have higher component density, more components with compact sizes and become more complicated than before. For many applications, such as healthcare devices and micro print head, it’s difficult to find a reliable heating technology to fit in the electronic design of these devices for controllable precision heating on very small spot. Murata now has already commercialized the FTP series PTC microheaters in the world’s smallest size at 1.6 x 0.8 x 0.68 mm for such special heating needs. The microheaters are ultra-compact PTC ceramic chip heaters that aim at the following applications:
- Healthcare;
- Medical appliances;
- Consumer electronics;
- General electronic appliances;
- Instrumentation;
- Beauty;
- Camera Lens and Mirror anti-fog;
- Temperature compensation circuitry;
- Paper dryer for PPC printer;
The Murata microheaters have high heat response because of the small size. The Murata PTC microheaters generate heat with very low voltage to heat a small volume of space, the high heating response helps improve greatly the heating efficiency, thus save much energy. With low-power and energy-saving design, the PTC microheaters can be powered by an AA size battery at 1.5VDC. With the nature of PTC ceramics, the microheater temperature can be self-controlled to prevent high temperature fluctuation away from the Curie point of the device. This characteristic offers simplicity and safety for using the devices in new circuit designs. The nominal resistance at 25 °C of the Murata FTP series PTC microheaters ranges from 2.2 Ω up to 68 Ω requiring an operating voltage from 2.0V up to 6.0V by different microheaters.
The FTP series of PTC microheaters are offered in the ultra-compact 1608 footprint. The microheaters have flat top surface that is made of insulating epoxy to allow direct contact to the components to be heated.
The ultra-compact size of these microheaters also make them suitable for spot-heating or compensation in a very tight area. The PTC microheaters offer electronic design engineers great freedom of design.
In application designs, we can use a PNP low-dropout regulator topology with feedback and error amplifier to drive the microheater and maintain it at the preset temperature. The following circuit shows the concept of implementing such a precision closed-loop temperature control of the PTC microheater. The circuit consists of a PNP BJT as the pass element. The feedback loop consists of a voltage divider that tracks the voltage change on the NTC thermistor due to temperature changes. The error between the preset setting point and the NTC measurement will be compared by the op amp and the output of the comparator circuit is used to turn on/off the PNP transistor. To avoid nuisance, we add about ± 0.5 °C hysteresis to the setting point at 80 °C. The result is shown below by the plots.
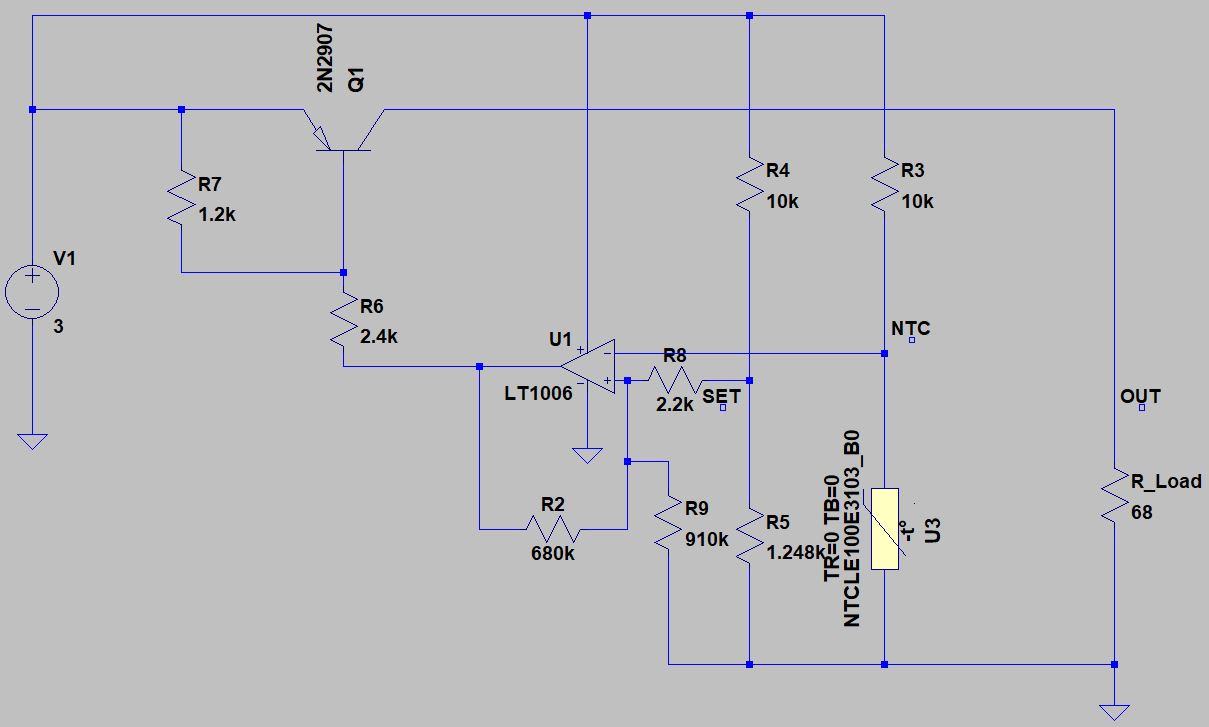
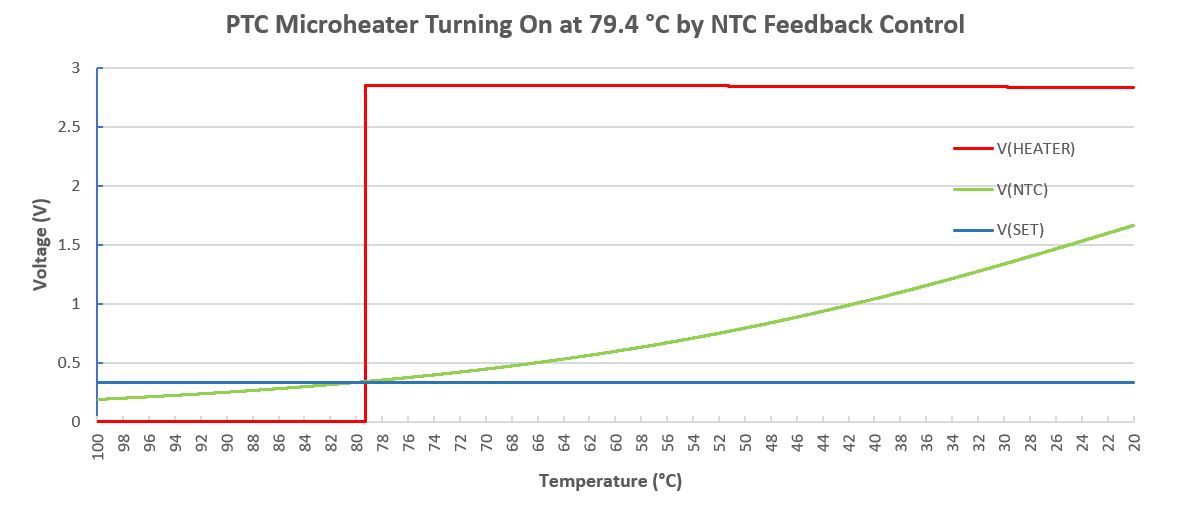
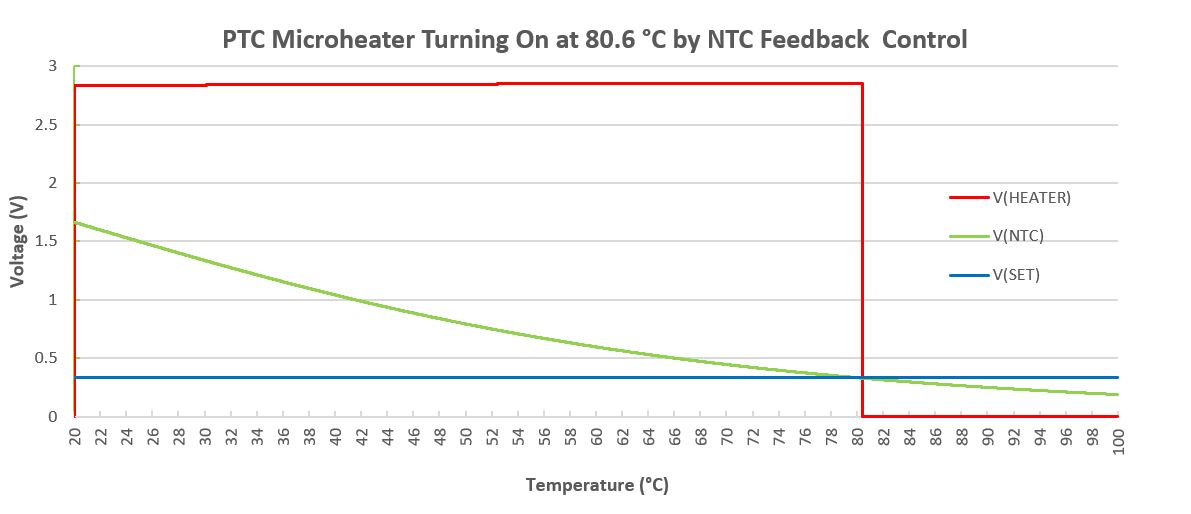
Read more at: https://www.murata.com/en-global/products/sensor/guide/sensorguide3/sensorguide/ftp_series





